USG & CT GUIDED FNAC/BIOPSY
USG & CT GUIDED FNAC/BIOPSY
Why it is necessary:
To identify the etiology of a lump or mass, or other abnormal condition in the body.
How it performed:
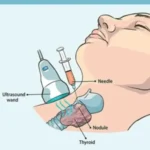
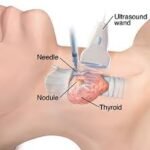
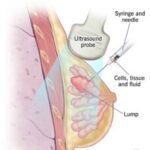
- Doctor inserts a small needle, guided by USG, CT or other imaging techniques, into the abnormal area without causing any harm into adjacent vital structure.
- A sample of tissue is removed and given to a pathologist, who looks it under a microscope to determine what the abnormality is — for example, cancer, a noncancerous tumour, infection, or inflammation.
What are the benefits:
- Precise location of abnormality under imaging guidance
- Chances of positive results increased significantly
- Minimal damage to adjacent structure
What are the risks:
- Bleeding (2-3 %, in some location even less)
- Pneumothorax (in lung biopsy, 2-3 %)
-
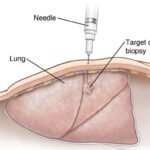
- Lateral cross section of chest showing fine needle aspiration of lung lesion. SOURCE: 60116A, also used in 10A11722 MOD: Moved lesion, extended needle, re-vignetted National Cancer Institute (2007). Image of Fine needle aspiration biopsy. Retrieved from WWW 9/18/07 at: http://www.meb.uni-bonn.de/cancer.gov/Media/CDR0000531057.jpg